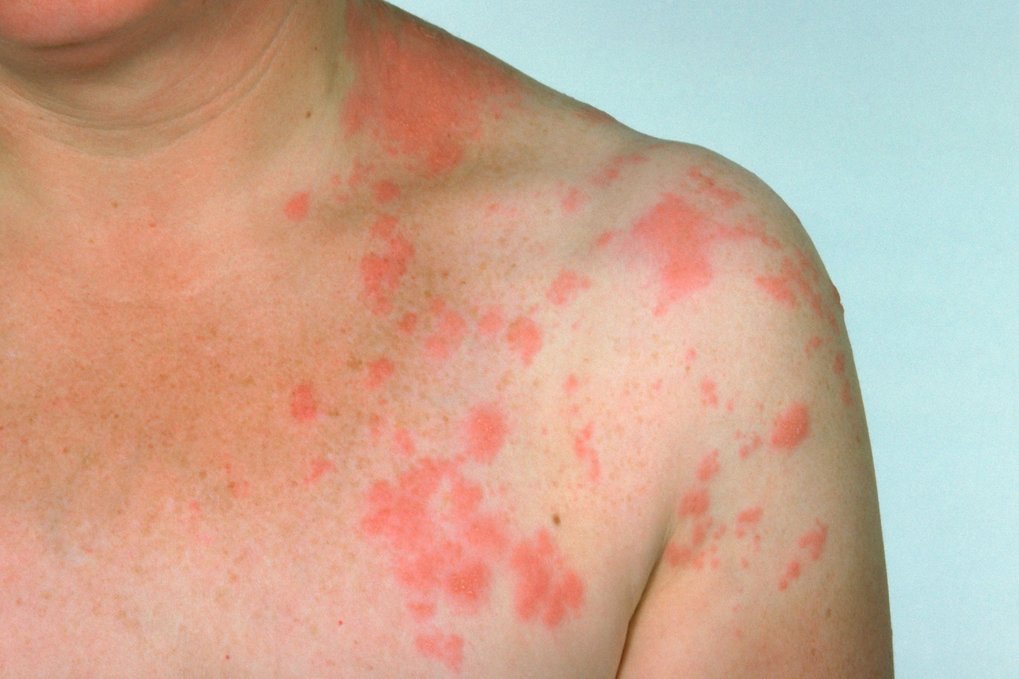
Shingles
Shingles is a painful viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus and affects adults who have previously had chickenpox. A shingles rash results from activation of dormant chicken pox virus particles, often many decades after the initial chicken pox infection. Shingles is contagious- the virus can spread through direct contact with fluid from blisters and this fluid can cause chicken pox in people who are susceptible to it.
What are the symptoms of shingles?
Shingles can be a very painful and uncomfortable rash on one side of your body or over one side of your face, including the eye. The pain can sometimes continue after the initial rash has healed, sometimes lasting for years. The symptoms of shingles include:
- Rash: Within a few days of feeling initial sensation changes to the skin, a red, blistering rash typically appears, most commonly on the torso, although it can also affect the face, eyes or other areas.
- Pain: Shingles often begins with pain or discomfort, which can be burning, tingling, numbness, stabbing or itching of the skin in the affected area. The pain is usually on one side of the face or body as it follows a specific nerve pathway. This pain can then continue when the rash has appeared, in the vicinity of the rash and in some cases continues long after the rash has disappeared. The intensity of the pain can vary from very mild to severe. It can be dull and throbbing or can include occasional sharp stabbing pains.
- Fluid-filled blisters: The rash can be accompanied by fluid, blood or pus-filled blisters, which can be very painful. Over time the blisters may burst, ooze, and eventually crust over.
- Itching: The rash and blisters may cause itching.
- Skin sensitivity: The affected skin can become very sensitive to touch and even the lightest touch or breeze may cause discomfort.
- Flu-like symptoms: Some individuals with shingles may experience flu-like symptoms, including chills, fever, fatigue and headache.
- Eye involvement: If shingles occurs around the eye, it can lead to symptoms such as redness, pain and vision problems.
The most common causes of shingles:
Shingles is the same virus that is responsible for chicken pox. After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in nerve cells. In some cases, many years later, the virus can reactivate, leading to the development of shingles. The exact cause is not always clear, but common triggers for shingles can be:
- Weakened immune system: This can result from various factors such as illness or medications that suppress the immune system.
- Aging: The risk of developing shingles increases with age due to an age-related reduction of effectiveness of the immune system.
- Stress: High levels of physical or emotional stress can weaken the immune system and potentially trigger reactivation of the dormant virus.
How to treat shingles symptoms yourself at home:
- Take paracetamol to ease the pain if required
- Keep the rash clean and dry – this will reduce the risk of infection
- Wear loose fitted clothing.
- Use a cool compress a few times a day
- Do not let any dressings or plasters stick to the rash
- Do not use antibiotic cream as this slows the healing process